Synchronous measurement of knee joint kinematics and kinetics
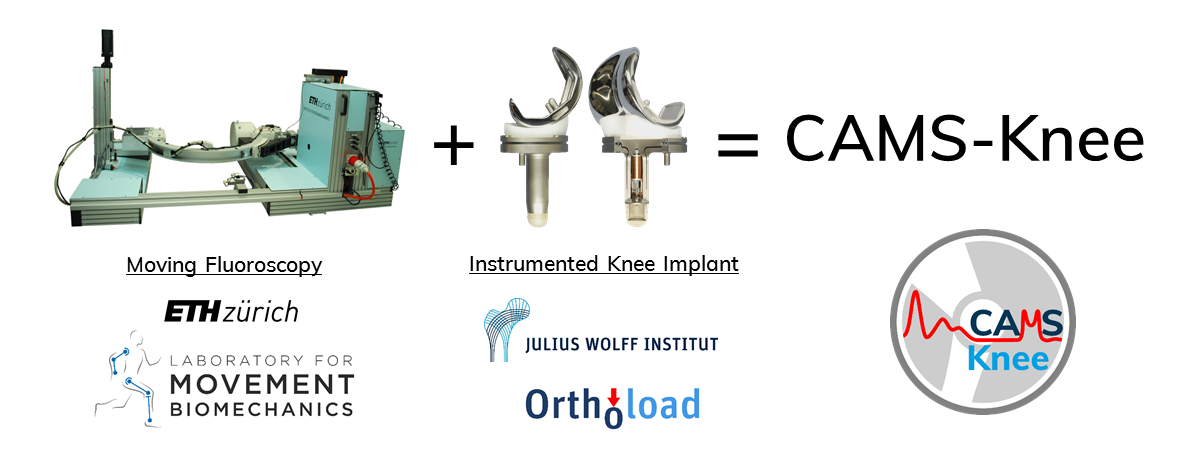
Knowledge of the internal joint loading and movement following total knee replacement is necessary in order to understand implant stability, wear mechanisms, and loading of the surrounding soft tissue structures. In order to achieve a deeper understanding of knee joint biomechanics, the CAMS-Knee project provides synchronous data of the following measures:
- TKR loading (instrumented implants, three forces and three moments)
- TKR kinematics (moving fluoroscope, 3D reconstruction of tibio-femoral implant kinematics)
- Whole body kinematics (marker-based movement analysis)
- Ground reaction forces (force plate data)
- EMG (lower limb, 16 channel)
- Video (patient movement)
- Multiple subjects, multiple activities, multiple repetitions
Specifically, the data was collected by combining two unique technologies:
- Use of the moving fluoroscope from the Institute for Biomechanics, ETH Zürich, allows dynamic tracking and imaging of the skeletal structures of the knee joint during a variety of activities of daily living, including normal walking, stair descent and ramp descent.
- Subjects from the Julius Wolff Institute, Berlin, each possess an instrumented knee prosthesis, which is able to telemetrically transfer internal joint contact forces that occur across the knee.
- The unique cohort of 6 subjects from the Julius Wolff Institute, Berlin, underwent comprehensive kinematic and kinetic testing at the Institute for Movement Biomechanics, ETH Zürich.
- The project is coordinated and supervised by Prof. Dr. William R. Taylor (ETH Zürich) and Dr.-Ing. Philipp Damm (Julius Wolff Institute, Berlin)


